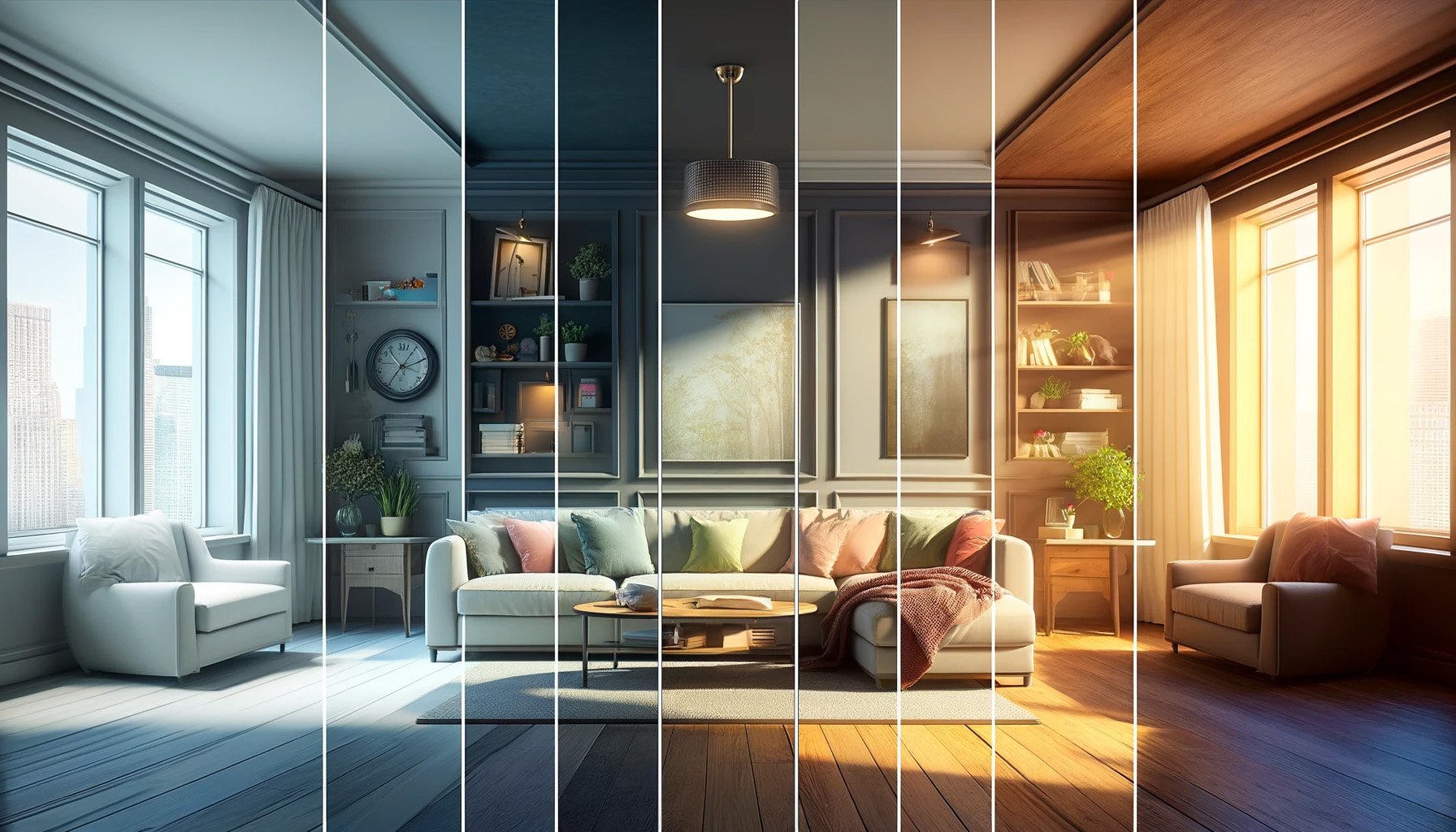
Light interaction with various surfaces.
Light interacts with different surfaces in nature through reflection, refraction, and absorption. These interactions are governed
by the light ray model, which assumes light travels in straight lines and behaves predictably when encountering different media.
Reflection: Light reflects off surfaces, changing direction while following the law of reflection, where the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
Refraction: When light passes from one medium to another (e.g., air to water), it bends. This bending depends on the relative
densities of the media and the angle of incidence. Light refracts away from the normal when moving from a more dense to a less
dense medium, and towards the normal when moving from a less dense to a more dense medium.
Absorption: Light can be absorbed by the surface it encounters, which converts the light energy into another form, like heat.
The behaviour of light is also influenced by the type of interface it encounters and the physical characteristics of the materials involved.
For instance, the critical angle of incidence can lead to total internal reflection when light attempts to move from a denser to a less dense medium.
These principles govern the pathways of light as it moves through both natural surfaces and interior spaces, giving rise to the rich
variety of visual and thermal experiences we encounter in our surroundings.